Liberty Timing File (.lib) in VLSI Design & Verification Flow
What is Liberty Format ?
Lib file is a short form of Liberty Timing file. Liberty syntax is followed to write a .lib file. LIB file is an ASCII representation of timing and power parameter associated with cells inside the standard cell library of a particular technology node. Liberty format is an industry standard format used to describe library cells of a particular technology. A cell could be a standard cell, IO Buffer, complex IP etc. Library cell description contains a lot of information like timing information, power estimation, other several attributes like area, functionality, operating condition etc. Speaking more technically, liberty format is a format to represent timing and power properties of black boxes (which we cant descend into). Liberty is an ASCII format, usually represented in a text file with extension “.lib“. In this section, we will discuss timing aspects (delay and transition times) related to liberty forma
Structure of the Liberty Format
The information inside the Lib file can be divided into two main parts, in the first part, it contains some information which is common for all the standard cells. To understand it better have a look in the following snapshot of the Lib file.
The common part of Lib file contains:
- Library name and technology name
- Units (of time, power, voltage, current, resistance and capacitance)
- Value of operating condition ( process, voltage and temperature) – Max, Min and Typical
Based on operating conditions there are three different lib files for Max, Min and Typical corners. In the second part of Lib file, it contains cell-specific information for each cell. The part of Lib file which contains cell-specific information is shown below.

Cell-specific information in Lib file is mainly:
- Cell name
- PG Pin name
- Area of cell
- Leakage power in respect of input pins logic state
Pins Details:
-
- Pin name
- Pin direction
- Internal power
- Capacitance
- Raise capacitance
- Fall Capacitance
- Fanout load
A snapshot of Lib file for the pin part is given below.

- CCS (Composite Current Source)
- NLDM (Non-Linear Delay Model)
How is Liberty File Populated with Data ?
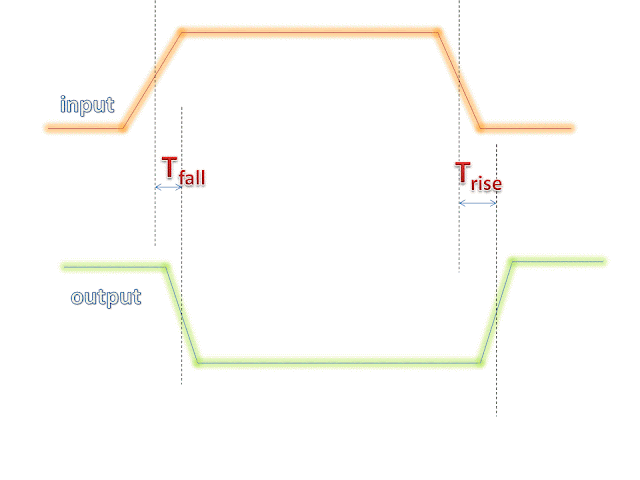
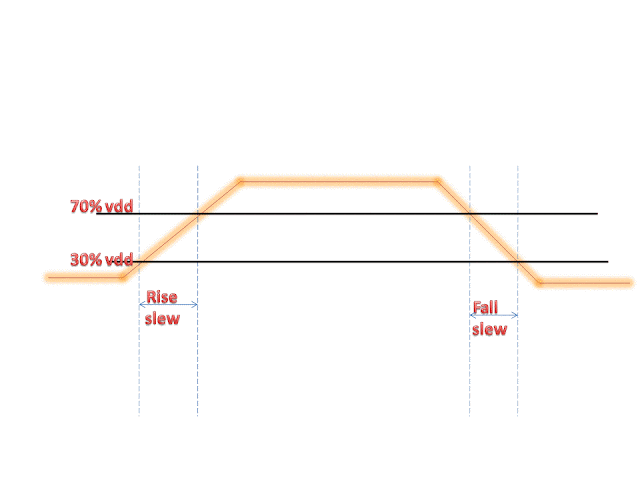
- Rise delay : It is the propagation delay between output and input when output changes from 0 to 1.
- Output fall delay : It is the propagation delay between output and input when output is changing from 1 to 0.
input_threshold_pct_fall : 50.0 ;# threshold point of input rising edge
input_threshold_pct_rise : 50.0 ;#threshold point of output falling edge
output_threshold_pct_fall : 50.0 ;#threshold point of output rising edge
output_threshold_pct_rise : 50.0 ;
V = Vdd * [ 1 – e^ ( -t/(RC ) ) ]
Difference Between PDK (Process Development Kit) and DDK (Digital Design Kit)
PDK is for Analog Designers or for Custom IC Layout Designers(Mainly to use with Cadence Virtuoso Tools or Synopsys Custom Compiler).
Standard Cell Library is for Digital Designers or for Digital Design & Verification Flow (To use with tools such as Synopsys Design Compiler/Fusion Compiler, Cadence Genus etc.)
PDK is nothing but Process Development Kit. PDK will have Pcell’s, transistor models etc.
DDK is Digital Design Kit. Standard Cell Library contains all the primitive cells that are requested by the Physical Design Engineers.
Standard Cell Libraries: are the basic building block of any advance digital IC, they contain all the combinational & sequential digital & mixed signal cells which will be used for the creation of SOC or ASIC. These cells will be arranged & connected in an orderly & meaningful pattern by using synthesis tools such as Fusion Compiler or Design/RTL Compiler(Synopsys), later on these cells along with other hard & soft marcos are used to create complete SOC. Normally people term .lib as Standard cell but they are wrong because Standard lib contains GDS2, DEF, LEF, (timing, power area & cap info of cells in .lib syntax), milkyway data base (FRAM, CEL etc.), CDL & RC-info in extracted netlist, noise info in celtic or ccsn format, voltage storm views etc. These are used at different stages of ASIC design by different EDA tools.
PDK: its definition varies from company to company what I know is PDK (Process Development Kit) contains info about the process for which the SOC or ASIC is been targeted, they are been even used to create even Standard cells, Memories, I/O’s & Analog portion typically they contains DRC, DFM, Antenna, LVS & extraction rule decks, along with SPICE models which are used during simulations. All the DRC & DFM info is been used to create P-cells (Cadence nomenclature) which are used in Cadence Virtuoso.
Video – PDK/DDK in VLSI Physical Design
Video – What is Standard Cell Characterization & How Liberty File .lib is Created?
References
Standard Library Cells Development – VTVT University